How to Prepare a Trial Balance in 5 Steps

To prepare a trial balance, you need to list the ledger accounts along with their respective debit or credit amounts. This is done to determine that debits equal credits in the recording process
The trial balance is the first step toward recording and interesting your financial results. Preparing the trial balance perfectly ensures that the final accounts are error-free.
What this article covers:
- How Does a Trial Balance Work?
- How Do You Prepare a Trial Balance?
- What Are the Methods of Preparing Trial Balance?
- How Are Accounts Listed in Trial Balance?
- How Do You Match a Trial Balance?
How Does a Trial Balance Work?
In a double-entry account book, the trial balance is a statement of all debits and credits.
Since each transaction is listed in a way to ensure the debits equaled credits, the quality should be maintained in the general ledger and the trial balance. If the sum of debits does not equal the sum of credits, an error has occurred and must be located.
Businesses prepare a trial balance regularly, usually at the end of the reporting period to ensure that the entries in the books of accounts are mathematically correct.
It is also important to note that even when the trial balance is considered balanced, it does not mean there are no accounting errors. For example, the accountant may have failed to record an account or classified a transaction incorrectly. These are accounting errors that would not show up in the trial balance.

How Do You Prepare a Trial Balance?
To prepare a trial balance, you will need the closing balances of the general ledger accounts. The trial balance is prepared after posting all financial transactions to the journals and summarizing them on the ledger statements. The trial balance is made to ensure that the debits equal the credits in the chart of accounts.
- Before you start off with the trial balance, you need to make sure that every ledger account is balanced. The difference between the sum of all the debit entries and the sum of all the credit entries provides the balance.
- Prepare an eight-column worksheet. The column headers should be for the account number, account name and the corresponding columns for debit and credit balances.
- For every ledger account, transfer to the trial balance worksheet the account number and account name along with the account balance in the appropriate debit or credit column.
- Add up the amounts of the debit column and the credit column. Ideally, the totals should be the same in an error-free trial balance. When the totals are same, you may close the trial balance.
- If there is a difference, accountants have to locate and rectify the errors.
Here are some instances of errors in the trial balance.
- Entries have been made twice
- Omission of entries
- Entries have been made to the wrong account
- Transposition error
- A mistake in transferring the balances to the trial balance
- Error in balancing an account
- The wrong amount is posted in the ledger
- Made the entry in the wrong column, debit instead of credit or vice versa
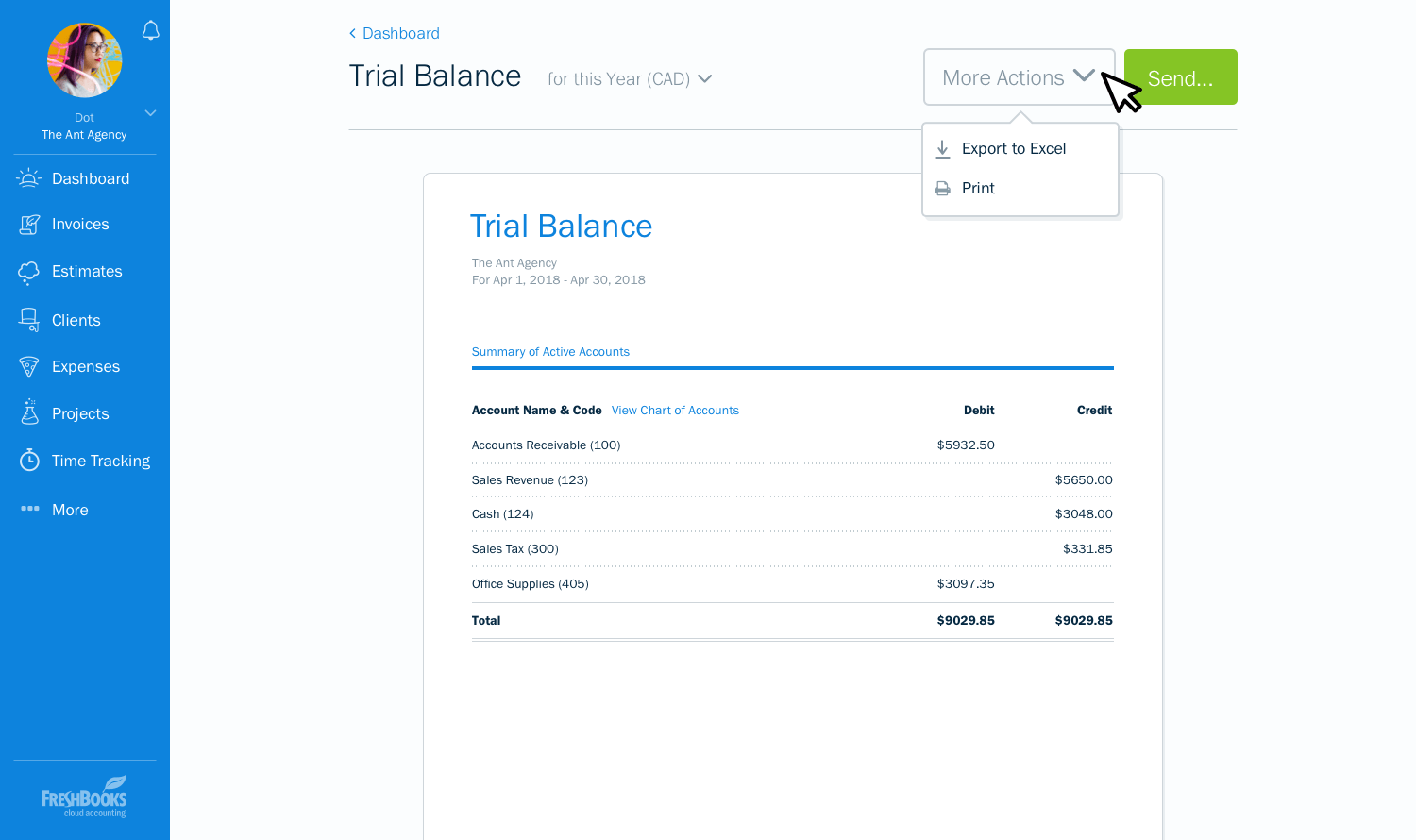
Source: https://www.uat.freshenv.com/blog/introducing-general-ledger
What Are the Methods of Preparing Trial Balance?
There are two primary methods of preparing the trial balance.
Total Method
The debit side and credit side of ledger accounts are added up. The total of the debit side is placed in the debit column and the total of the credit side in the credit column of the trial balance. The total of the debit column and credit column should be the same.
Balance Method
Under balance method, only the balances of all the ledger accounts are shown in the trial balance.

How Are Accounts Listed in Trial Balance?
The trial balance accounts are listed in a specific order to help in the preparation of financial statements.
Accounts in a trial balance are listed in the following order:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Revenue
- Expenses
Furthermore, the assets and liabilities have to be listed in order of liquidity, which refers to how quickly an asset can be converted to cash to pay off liabilities. The most liquid assets are listed first. This includes cash and short-term accounts receivables.
How Do You Match a Trial Balance?
The purpose of a trial balance is to ensure all the entries are properly matched. If the trial balance totals do not match, it could be the result of a discrepancy or accounting error. This is an unadjusted trial balance.
Before the errors can be identified and corrected, a temporary suspense account is created to match the trial balance totals temporarily.
Once the errors are located, adjusting entries are posted to the trial balance. Once this is done, the trial balance is considered an adjusted trial balance.
Preparing a trial balance regularly helps a business in spotting errors in its books. With accounting software, business owners don’t have to wait for the end of the year to make a trial balance and assess their financial information.
RELATED ARTICLES

 What Is a Trial Balance Report?
What Is a Trial Balance Report? What Is a General Ledger Report?
What Is a General Ledger Report? How to Improve Business Performance: Business Performance Management Tips
How to Improve Business Performance: Business Performance Management Tips Business Performance Report: How to Write a Business Performance Report?
Business Performance Report: How to Write a Business Performance Report? How to Write an Annual Report: 4 Tips for Getting Started
How to Write an Annual Report: 4 Tips for Getting Started How to Prepare Accounts Receivable Aging Reports?
How to Prepare Accounts Receivable Aging Reports?